The research of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas shielded welding started in 1955 and put into production practice in 1960. For half a century, CO2 gas shielded welding has been widely used in shipbuilding, locomotive manufacturing, automobile manufacturing, petrochemicals, engineering machinery, agricultural machinery, etc. CO2 gas shielded welding has become one of the most important fusion welding methods today.
Definition of gas shielded welding Gas shielded welding belongs to the fusion welding method which uses an arc as a heat source. In the fusion welding process, in order to obtain a good quality weld, the welding zone must be effectively protected from the intrusion of harmful gases in the air; in order to meet the needs of the welding metallurgy process, a gas protection form is used. The use of gas-shielded gas-shielded arc welding can reliably guarantee the welding quality and make up for the limitations of manual arc welding. In addition, gas-shielded welding has unique advantages in thin plates and efficient welding, so it is used in welding production. Applications are becoming increasingly widespread. An arc welding method using an external gas as an arc medium and protecting the arc and the welding zone is called gas shielded arc welding, or gas shielded welding for short. Gas shielded welding directly relies on the airflow continuously sent from the nozzle, which creates a local gas protection layer around the arc, so that the electrode end, the droplets and the molten pool metal are in the protective gas shield, and the air is mechanically isolated from the welding area. Ensure the stability of the welding process and obtain good quality welds.
An arc welding method using an external gas as an arc medium and protecting the arc and the welding zone is called gas shielded arc welding, or gas shielded welding for short. Gas shielded welding directly relies on the airflow continuously sent from the nozzle, which creates a local gas protection layer around the arc, so that the electrode end, the droplets and the molten pool metal are in the protective gas shield, and the air is mechanically isolated from the welding area. Ensure the stability of the welding process and obtain good quality welds.
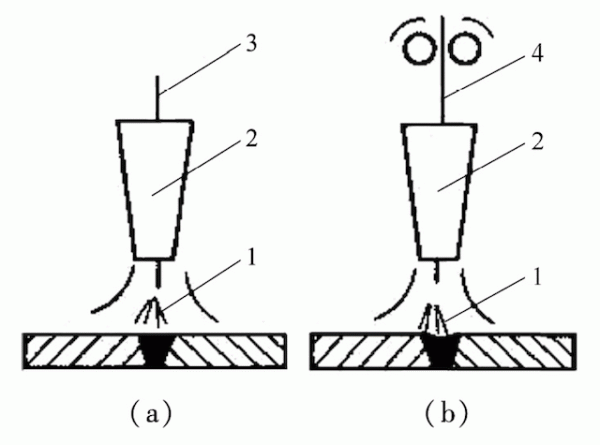
There are two different types of gas shielded welding according to the electrode material used (Figure 11): one is arc welding with a non-melting electrode (tungsten electrode), which is called non-melting electrode gas shielded welding; the other is Arc welding with one or more melting electrodes (wires) is called melting electrode gas shielded welding.
Second, the characteristics of gas shielded welding
Compared with other arc welding methods, gas shielded welding has the following characteristics:
(1) When using open-arc welding, flux is generally not necessary, so the molten pool has good visibility and is easy to operate; moreover, the protective gas is sprayed, which is suitable for all-position welding, and is not restricted by the spatial position, which is beneficial to the mechanization of the welding process And automation. (2) Due to the heat concentration of the arc under the compression of the protective airflow, the welding pool and the heat affected zone are small, so the deformation and cracking tendency of the weldment are not large, and it is especially suitable for welding of thin plates.
(3) When using inert gas protection such as argon and helium, when welding more active metals or alloys, the welding quality is very high.
(4) There must be special windproof measures for outdoor work, otherwise the protection effect will be affected; the light radiation of the arc is strong and the welding equipment is more complicated.
(5) The welding process is easy to operate, there is no slag or very little slag, and slag removal is basically not required after welding. No or very little spatter during welding.
(6) Pulse welding can be realized to reduce heat input.
Third, the working principle of CO2 gas shielded welding
Using an automatic wire feeding mechanism to feed the wire to the molten pool, an arc is formed between the welding wire and the workpiece, and the method of gas shielded under the protection of CO2 gas is called CO2 gas shielded welding, referred to as CO2 welding. It is an advanced welding method using CO2 gas sprayed from the nozzle to isolate the air and protect the molten pool. The welding process and working principle are shown in Figure 12.
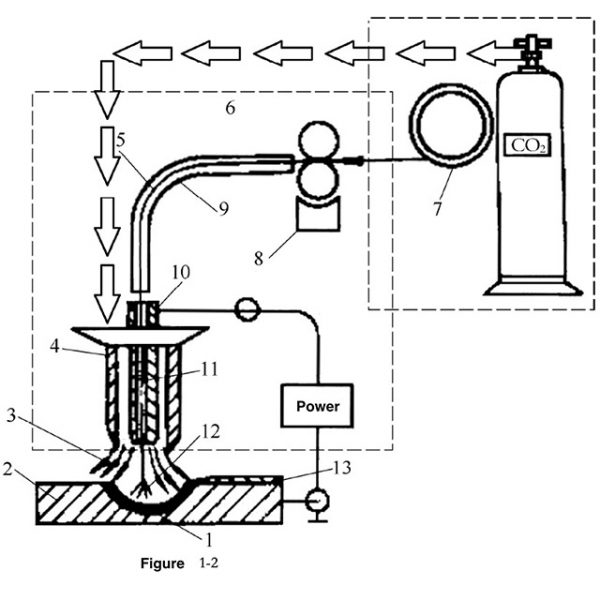
CO2 gas shielded welding belongs to active gas shielded welding, so it is also called MAG welding or MAGC welding. The CO2 gas ejected from the nozzle is decomposed into CO at a high temperature and emits O2. Under welding conditions, CO2 and O2 can oxidize iron and other alloying elements, resulting in spatters and CO pores during welding. The higher the temperature, the higher the decomposition rate of CO2, the more O2 released, and the more serious the problem. . Therefore, when conducting CO2 gas shielded welding, measures must be taken to prevent the burning of alloy elements in the base metal and the welding wire and other welding defects.